International trade as a tool to alleviate poverty
International trade fuels global economic growth and in turn helps in eradicating poverty. A free-flowing global economy is making it possible for millions to escape extreme poverty. The present article focuses on the influences of international trade on economic activities as well as growth. Hence, it analyses international trade as a tool to alleviate poverty.
The benefits of trade for the underprivileged can be maximised by lowering transaction costs mostly borne by workers and consumers. Trade also helps men and women in rural communities to overcome poverty. Globalised economies tend to develop more quickly, innovative and productive. They are also able to give their citizens more opportunities to generate high income than their closed counterparts.
By providing affordable goods and services, trade also benefits lower-income households. International trade provides opportunities to export goods and services to countries with high demand. It generates employment in small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) which in turn increases well-being. Hence, international trade, on the one hand, replaces high-cost domestic goods and services with imported goods, on the other hand, gives better prices for domestically produced goods and services in the international market.
How it impacts the well-being of the poor?
- Increasing consumer access to new and affordable commodities. The free flow of capital and labour provides better remuneration to skilled workers and reduces the cost of capital.
- Increasing the government’s ability to support programs for the poor by giving sources of revenue through taxes and tariffs.
- Providing incentives for investment and innovation
- Reducing the vulnerability of an economy to harmful external shocks
Trade also promotes economic growth by promoting resource allocation based on the perceived comparative advantages of participating nations.
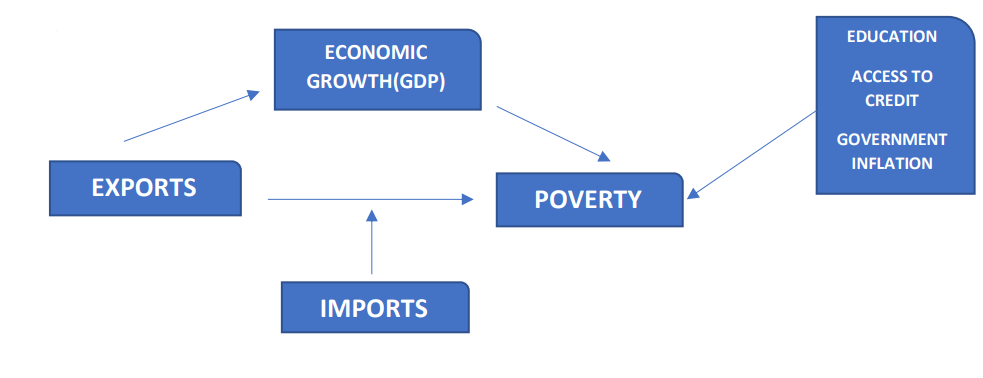
Trade results in increases in productivity and efficiency due to labour specialisation, free exchange, and availability of a wider range of goods and services. A sizable portion of the workforce in many emerging and impoverished countries is unskilled and underpaid. Therefore, exports of domestic goods and services create jobs for unskilled labour and provide a chance to gain skills with quality education.
Therefore, trade has a positive impact on reducing poverty and inequality by increasing productivity, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), and creating jobs. It has significant policy implications for the growth and development of the country and the well-being of the people.

Author: Prerana K. Jain The author is a PhD research scholar in economics at ICFAI Business School, Hyderabad.


Very insightful 😊👍
Brilliantly written and point to point understanding of the scenario with limited words used
Superb job…very fine work. Keep it up!!
You made easy to understand ma’am
Thank you!!
I found your observation about suppression of poverty by improvising trade to be insightful.
If I give a thought about it, your reasoning makes sense and it is acceptable. I would take a moment to appreciate your effort on this study.