An Introduction to the Budget, Its Components and Types of Budget
Budget: an introduction
The whole article is divided into an introduction to the budget, its components and types of budget. Budget is a statement of estimated expenditures and receipts of the government for a financial year. It is a detailed plan of all the economic activities of an economy and is generally prepared in the light of past experience. We have a union budget in India, where the various amount of money is allocated to the various sectors. There are two types of account, Revenue account and Capital account. Revenue account includes revenue receipt and revenue expenditure while the capital account includes assets and liabilities of the government.
Budget: Its Components
https://armisticeexpress.com/wif8e9wub?key=ecf0ef57aa689628e678e90b53cfaf9b
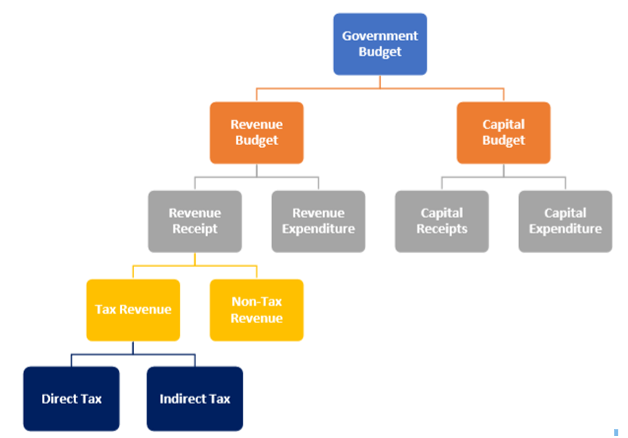
The terms in the flow chart are explained below-
Revenue Budget
The term Revenue budgets can be defined as forecasts of an entity’s revenues from sales and the expenditures incurred, including budget-related to capital.
Revenue Receipt: Revenue receipts are receipts of the government from different recursive sources such as taxes, interest, and dividend on government investment, cess and other receipts for services provided by the government. Following are the different types of revenue receipts.
- Tax Revenue: The term Tax revenue can be defined as the all revenues collected from various taxes on income and profits, social security contributions, different taxes levied on goods and services consumed, taxes on ownership of wealth and transfer of the property, and different types of other taxes.
- Direct Tax: Direct Tax refers to the tax paid directly by an entity to the imposing authority. This is the tax that cannot be transferred to the other entity.
- Indirect Tax: Indirect taxes refer to the taxes that are imposed by the government on goods and services consumed. In contrast to direct taxes, it can be shifted to the other entity who consumes it finally.
- Non-Tax Revenue: Non-Tax Revenue refers to the income of the government which is earned from the sources other than taxes. It is of recurring characteristics.
Revenue Expenditure: Revenue expenditure refers to the expenditure that is required for the normal running of various departments and services provided by the government, interest charges on debt incurred by the government, subsidies given to the various entity and so on.
Capital Budget
Capital budgeting can be defined as the planning process by the government used to determine the worthiness of long-term investments and projects funding of cash through the firm’s capitalization structure. This includes investments in new machinery, new plants, new products, and research development
Capital Receipts: The term capital receipts refer to the receipts of the government which results in either increase in liability or reduces the assets of the government.
Capital Expenditure: The term capital expenditure refers to the funds used by an entity to acquire, upgrade and maintain physical assets such as property, buildings, an industrial plant, technology or equipment.
Types of Budget
Outcome Budget: This was first established in 2005-06. This budget comprises of projects and schemes that provide information on outlays of all central organisation and departments. This type of budget is a performance budget of various ministries that handle the various development programs.
Zero-Based Budgeting: This type of budget practising was introduced by Peter Fiere. Each item in the budget is allocated on the basis of merit rather than preference. It is prepared under the assumption that there was a budget in the past.
Gender Budgeting: This was first introduced in 1984 in Australia. In India, gender budgeting was introduced in 2005-06. Its main objective was to mainstream budget based on the gender perspective of all sectoral programs and policies and also to empower women and gender justice.
Advantages of Budgetary Control
- Maximization of profits
- Co-ordination
- Specific aims
- Tool for measuring performance
- Introduction of incentive schemes

Author: Amrita Singh Post Graduate Student Central University of South Bihar


Commendable writeup ! Nicely introduced an oblivious reader to the concept of budget…
Very easy to get the concept..
Being a 11th student this was really helpful to me and I appreciate this alot
Super
Such an amazing and knowledgeable blog.. Keep posting such blogs..
Thankfully to the outhor. It help me as well as new commerce students for having a basic knowledge about budget concept.
Its a really good for knowledge
U r so nice mam everyone will understand your topic may god bless you for your knowledge level just keep it up mam
Very nicely explained👍
Thankfully to the outhor. It help me as well as new commerce students for having a basic knowledge about budget concept.
Such an amazing and knowledgeable blog.. Keep posting such blogs..
Great article . The things are explained in simple and compact form. I really liked how you divided into point notes. It really helped to understand the topic.
I m the students of class 11and it was very helpful for me
This article is well versed, decorated and in the terms of conceptually clear. It will help to understand the budget and budget’s components. Honesty saying the article is reducing complexity of budget terminology. Keep posting such knowledgeable blogs.